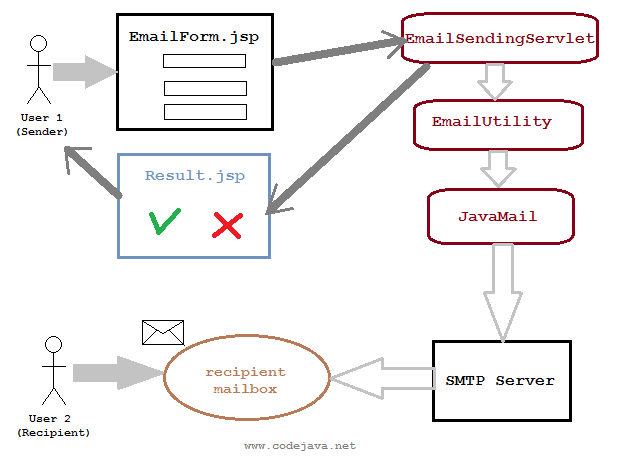
Sending e-mail with JSP, Servlet and JavaMail
| Print Email
Hot & New: Java Servlet, JSP and Hibernate: Build a Complete Website
Table of content:- Creating e-mail utility class
- Creating e-mail form in JSP
- Writing servlet for sending e-mail
- Configuring SMTP server
- Writing result page
- Test the application
- Download the application as Eclipse project
- How to start e-mail programming in Java for how to download and use JavaMail.
- Send e-mail in plain text using JavaMail for how to write code to send a simple e-mail message.
1. Creating e-mail utility class
Based on the article Send e-mail in plain text using JavaMail we write a utility class called EmailUtility.java as follows:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
| package net.codejava.email;import java.util.Date;import java.util.Properties;import javax.mail.Authenticator;import javax.mail.Message;import javax.mail.MessagingException;import javax.mail.PasswordAuthentication;import javax.mail.Session;import javax.mail.Transport;import javax.mail.internet.AddressException;import javax.mail.internet.InternetAddress;import javax.mail.internet.MimeMessage;/** * A utility class for sending e-mail messages * @author www.codejava.net * */public class EmailUtility { public static void sendEmail(String host, String port, final String userName, final String password, String toAddress, String subject, String message) throws AddressException, MessagingException { // sets SMTP server properties Properties properties = new Properties(); properties.put("mail.smtp.host", host); properties.put("mail.smtp.port", port); properties.put("mail.smtp.auth", "true"); properties.put("mail.smtp.starttls.enable", "true"); // creates a new session with an authenticator Authenticator auth = new Authenticator() { public PasswordAuthentication getPasswordAuthentication() { return new PasswordAuthentication(userName, password); } }; Session session = Session.getInstance(properties, auth); // creates a new e-mail message Message msg = new MimeMessage(session); msg.setFrom(new InternetAddress(userName)); InternetAddress[] toAddresses = { new InternetAddress(toAddress) }; msg.setRecipients(Message.RecipientType.TO, toAddresses); msg.setSubject(subject); msg.setSentDate(new Date()); msg.setText(message); // sends the e-mail Transport.send(msg); }} |
2. Creating e-mail form in JSP
A form for sending an e-mail message would contain the following fields at least:- Recipient address: text field.
- Subject: text field.
- Content: text area.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| <%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1" pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%><!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"><html><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"><title>Send an e-mail</title></head><body> <form action="EmailSendingServlet" method="post"> <table border="0" width="35%" align="center"> <caption><h2>Send New E-mail</h2></caption> <tr> <td width="50%">Recipient address </td> <td><input type="text" name="recipient" size="50"/></td> </tr> <tr> <td>Subject </td> <td><input type="text" name="subject" size="50"/></td> </tr> <tr> <td>Content </td> <td><textarea rows="10" cols="39" name="content"></textarea> </td> </tr> <tr> <td colspan="2" align="center"><input type="submit" value="Send"/></td> </tr> </table> </form></body></html> |
3. Writing servlet for sending e-mail
Now we implement a servlet that does the following tasks:- Read SMTP server settings from web.xml file.
- Take input from EmailForm.jsp page.
- Invoke the EmailUtility class to send an e-mail message.
- Return a response to the user.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
| package net.codejava.email;import java.io.IOException;import javax.servlet.ServletContext;import javax.servlet.ServletException;import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;/** * A servlet that takes message details from user and send it as a new e-mail * through an SMTP server. * * @author www.codejava.net * */@WebServlet("/EmailSendingServlet")public class EmailSendingServlet extends HttpServlet { private String host; private String port; private String user; private String pass; public void init() { // reads SMTP server setting from web.xml file ServletContext context = getServletContext(); host = context.getInitParameter("host"); port = context.getInitParameter("port"); user = context.getInitParameter("user"); pass = context.getInitParameter("pass"); } protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { // reads form fields String recipient = request.getParameter("recipient"); String subject = request.getParameter("subject"); String content = request.getParameter("content"); String resultMessage = ""; try { EmailUtility.sendEmail(host, port, user, pass, recipient, subject, content); resultMessage = "The e-mail was sent successfully"; } catch (Exception ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); resultMessage = "There were an error: " + ex.getMessage(); } finally { request.setAttribute("Message", resultMessage); getServletContext().getRequestDispatcher("/Result.jsp").forward( request, response); } }} |
Servlet and JSP (A Tutorial) [Kindle Edition] - This book covers everything in Servlet and JSP in a concise and easy to understand way. Every Java programmer should understand the pillar stones of Servlet and JSP before diving into other web frameworks which are built on top of Servlet and JSP.
4. Configuring SMTP server
We configure the settings for SMTP server in the web deployment descriptor file (web.xml) as follows:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:web="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0"> <display-name>EmailSendingWebApp</display-name> <!-- SMTP settings --> <context-param> <param-name>host</param-name> <param-value>smtp.gmail.com</param-value> </context-param> <context-param> <param-name>port</param-name> <param-value>587</param-value> </context-param> <context-param> <param-name>user</param-name> <param-value>YOUR_EMAIL</param-value> </context-param> <context-param> <param-name>pass</param-name> <param-value>YOUR_PASSWORD</param-value> </context-param> <welcome-file-list> <welcome-file>EmailForm.jsp</welcome-file> </welcome-file-list></web-app> |
.
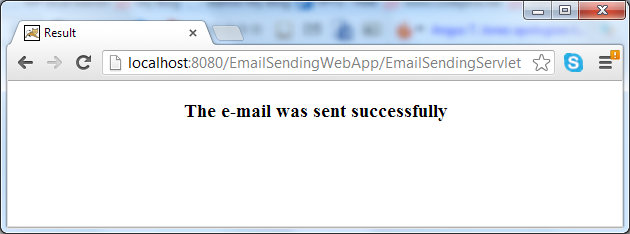
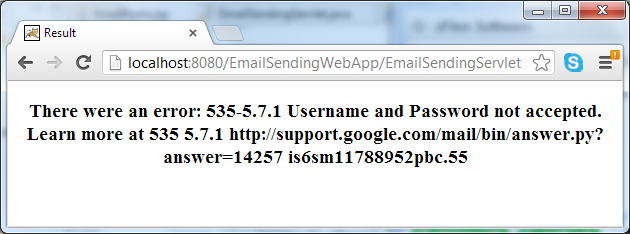
5. Writing result page
Code of the Result.jsp page is as simple as follows:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| <%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1" pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%><!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"><html><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"><title>Result</title></head><body> <center> <h3><%=request.getAttribute("Message")%></h3> </center></body></html> |
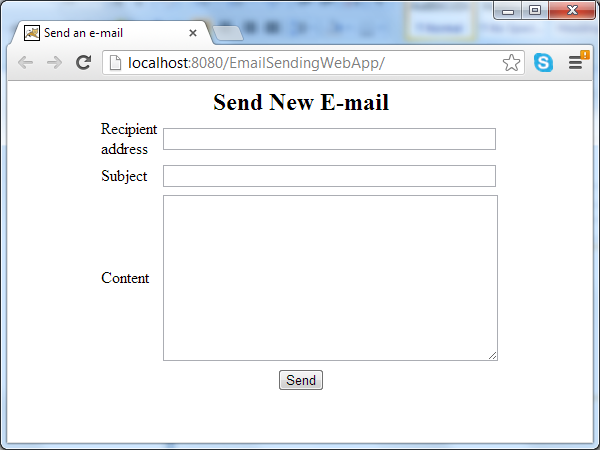
6. Test the application
Supposing the application is packaged as EmailSendingWebApp.war and is deployed on Tomcat server on localhost at port 8080. Type the following URL in your web browser:
http://localhost:8080/EmailSendingWebApp/
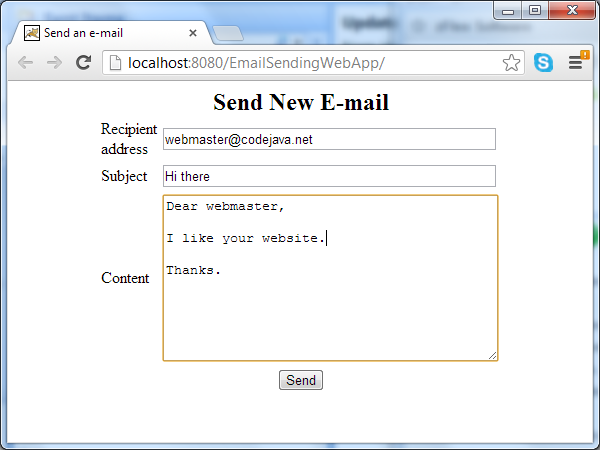
A form is displayed for entering message details. Type some information into the fields: